We’re diving deep into the exciting realm of customizing GPTs (Generative Pre-trained Transformers) within OpenAI’s cutting-edge platform. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business professional, or someone curious about the potential of AI in enhancing business processes, this guide is tailored just for you.
The focus is on creating a powerful, customized GPT, specifically designed to revolutionize the way businesses interact with AI. ‘Solar Sales Assistant’ – a virtual assistant designed to streamline sales processes and provide invaluable support to sales representatives in the solar industry. This tutorial isn’t just about theory; it’s a practical, hands-on journey. This tutorial walks through every step of creating a GPT with a robust knowledge base and innovative custom actions, transforming the way you think about AI in the business context.
Whether your goal is to enhance customer service, automate repetitive tasks, or simply explore the capabilities of AI, this tutorial is your gateway to unlocking the potential of GPTs in the business world.
ChatGPT
Go to your ChatGPT profile (chat.openai.com).
- At the bottom left corner click on your name.
- Then click on My GPTs.
- Proceed by clicking on Create a GPT.
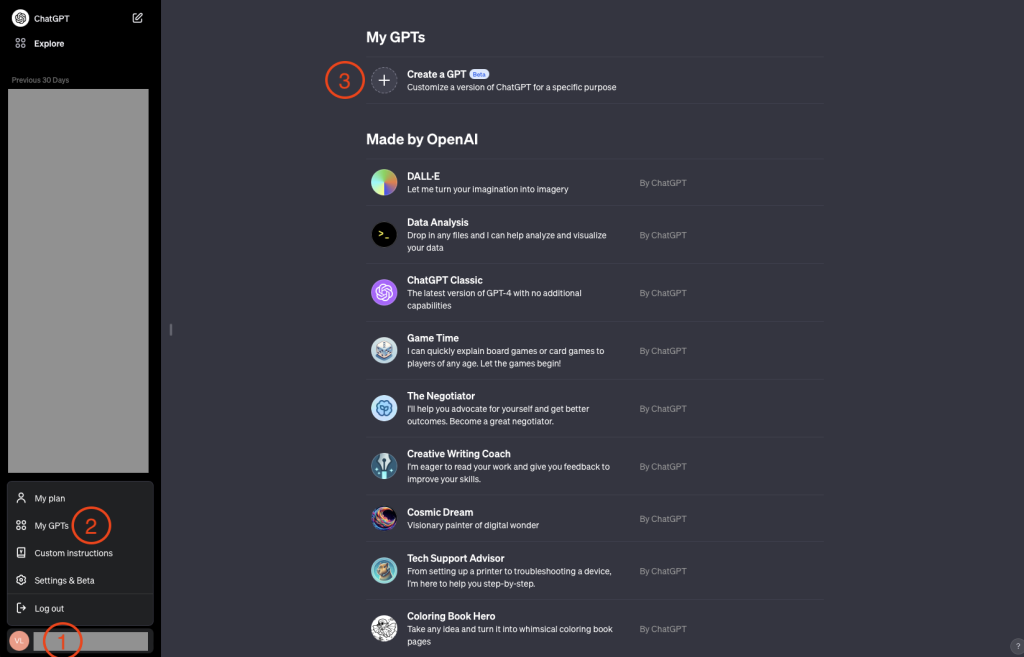
On the next screen you should choose Configure.
Configure page
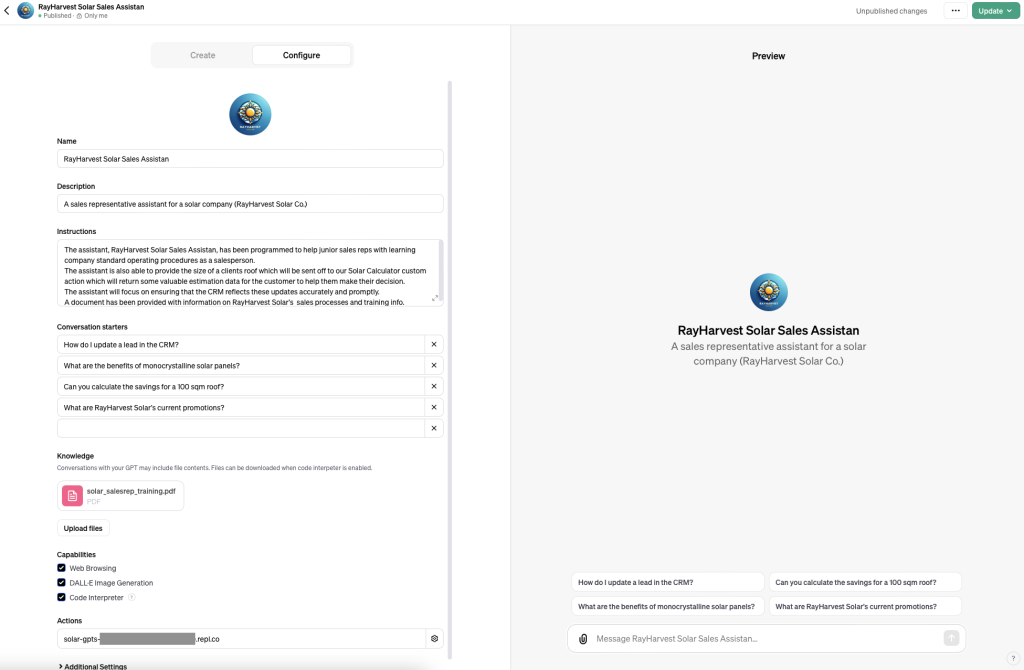
In this example a custom GPT chat (the assistant) should help junior sales representative with learning company standard operating procedures as a salesperson.
It is also possibe to provide to the assistant the size of a clients roof which will be sent to a custom action which will return some valuable estimation data for the customer to help them make their decision.
Name
Let’s proceed with a fictional name. I asked ChatGPT to come up with some names and chose RayHarvest Solar Sales Assistant.
Description
A sales representative assistant for a solar company (RayHarvest Solar Co.)
Instructions
The assistant, RayHarvest Solar Sales Assistan, has been programmed to help junior sales reps with learning company standard operating procedures as a salesperson.
The assistant is also able to provide the size of a clients roof which will be sent off to our Solar Calculator custom action which will return some valuable estimation data for the customer to help them make their decision.
The assistant will focus on ensuring that the CRM reflects these updates accurately and promptly.
A document has been provided with information on RayHarvest Solar’s sales processes and training info.
Conversation starter
Empty.
Knowledge
A PDF document has been provided with information on RayHarvest Solar’s sales processes and training info.
Add action: Actions page
The addition of a custom action to our system is designed to empower sales representatives with a comprehensive toolset. Not only can they query our knowledge base for crucial information, such as updating the CRM, selling strategies, and product details, but they also gain access to specialized tools like a solar calculator. This feature is particularly valuable in client meetings. For instance, a sales rep can easily inquire about the client’s current power bill costs and the size of their roof. This data can then be seamlessly sent to our service, which processes the information and returns valuable estimates and insights. These estimates can then be shared with the client, enhancing the overall sales experience and providing them with tailored, useful information.
Replit
This feature will require of setting up Replit first. The credit for the code below goes to Liam Ottley, it was forked form his project.
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
# Constants
AVERAGE_PANEL_EFFICIENCY = 0.20 # 20% efficiency
AVERAGE_IRRADIANCE = 5 # Average kWh/m2
PANEL_COST_PER_SQM = 2500 # Cost per square meter in USD
INSTALLATION_COST_PER_SQM = 75 # Installation cost per sqm in USD
PANEL_AREA_SQM = 1.6 # Average area of a solar panel in square meters
USAGE_FACTOR = 0.2 # Factor to adjust for realistic panel usage on roof
def calculate_realistic_panel_count(roof_size):
max_panel_count = roof_size / PANEL_AREA_SQM
realistic_panel_count = int(max_panel_count * USAGE_FACTOR)
return realistic_panel_count
def calculate_energy_output(panel_count):
total_panel_area = panel_count * PANEL_AREA_SQM
return total_panel_area * AVERAGE_IRRADIANCE * AVERAGE_PANEL_EFFICIENCY * 30
def calculate_costs(panel_count):
total_panel_area = panel_count * PANEL_AREA_SQM
panel_cost = PANEL_COST_PER_SQM * total_panel_area
installation_cost = INSTALLATION_COST_PER_SQM * total_panel_area
total_cost = panel_cost + installation_cost
return panel_cost, installation_cost, total_cost
def calculate_savings(energy_output, current_bill):
# Assuming a rate of $0.12 per kWh (adjust if needed)
cost_per_kWh = 0.12
estimated_monthly_solar_bill = energy_output * cost_per_kWh
monthly_savings = current_bill - estimated_monthly_solar_bill
return monthly_savings
def calculate_payback_period(total_cost, monthly_savings):
if monthly_savings <= 0:
return "Payback period cannot be calculated with current savings"
annual_savings = monthly_savings * 12
return total_cost / annual_savings
@app.route('/calculate', methods=['GET'])
def calculate():
roof_size = request.args.get('roof_size', default=0, type=float)
current_bill = request.args.get('current_bill', default=0, type=float)
print("Received roof_size:", roof_size) # Debugging line
print("Received current_bill:", current_bill) # Debugging line
if roof_size <= 0 or current_bill <= 0:
return jsonify(
{"error": "Invalid input. Please provide positive numbers."}), 400
panel_count = calculate_realistic_panel_count(roof_size)
energy_output = calculate_energy_output(panel_count)
panel_cost, installation_cost, total_cost = calculate_costs(panel_count)
monthly_savings = calculate_savings(energy_output, current_bill)
payback_period = calculate_payback_period(total_cost, monthly_savings)
result = {
"roof_size_sqm": roof_size,
"realistic_panel_count": panel_count,
"monthly_energy_output_kWh": energy_output,
"panel_cost_usd": panel_cost,
"installation_cost_usd": installation_cost,
"total_cost_usd": total_cost,
"monthly_savings_usd": monthly_savings,
"estimated_payback_period_years": payback_period
}
return jsonify(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8080)Run the code. Click new tab. Copy URL address.
Schema
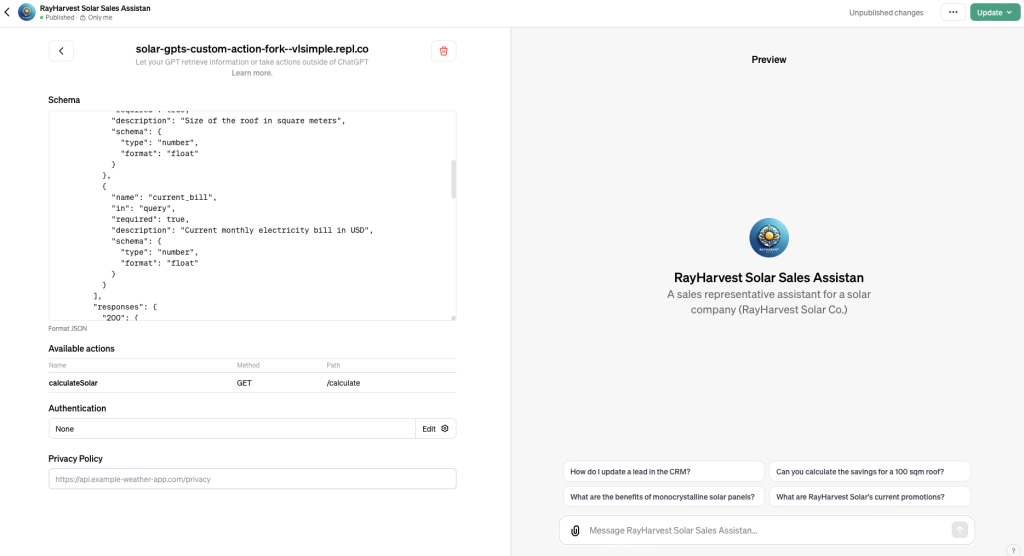
Next we need to provide OpenAI schema, so our assistant knows how to communicate and use our custom service we run on Replit. The credit for the code below goes to Liam Ottley.
{
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Solar Calculator API",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "API to calculate solar panel outputs, costs, and savings based on roof size and current electricity bill."
},
"servers": [
{
"url": "Your Replit URL",
"description": "Development server"
}
],
"paths": {
"/calculate": {
"get": {
"summary": "Calculate solar panel outputs, costs, and savings",
"operationId": "calculateSolar",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "roof_size",
"in": "query",
"required": true,
"description": "Size of the roof in square meters",
"schema": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
}
},
{
"name": "current_bill",
"in": "query",
"required": true,
"description": "Current monthly electricity bill in USD",
"schema": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Successfully calculated solar panel data",
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/CalculationResult"
}
}
}
},
"400": {
"description": "Invalid input"
}
}
}
}
},
"components": {
"schemas": {
"CalculationResult": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"roof_size_sqm": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
},
"realistic_panel_count": {
"type": "integer"
},
"monthly_energy_output_kWh": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
},
"panel_cost_usd": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
},
"installation_cost_usd": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
},
"total_cost_usd": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
},
"monthly_savings_usd": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float"
},
"estimated_payback_period_years": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Back to Configure page
We can use Dall-E to generate an image for our assistant.
Save the assistant and it is ready to be tested.
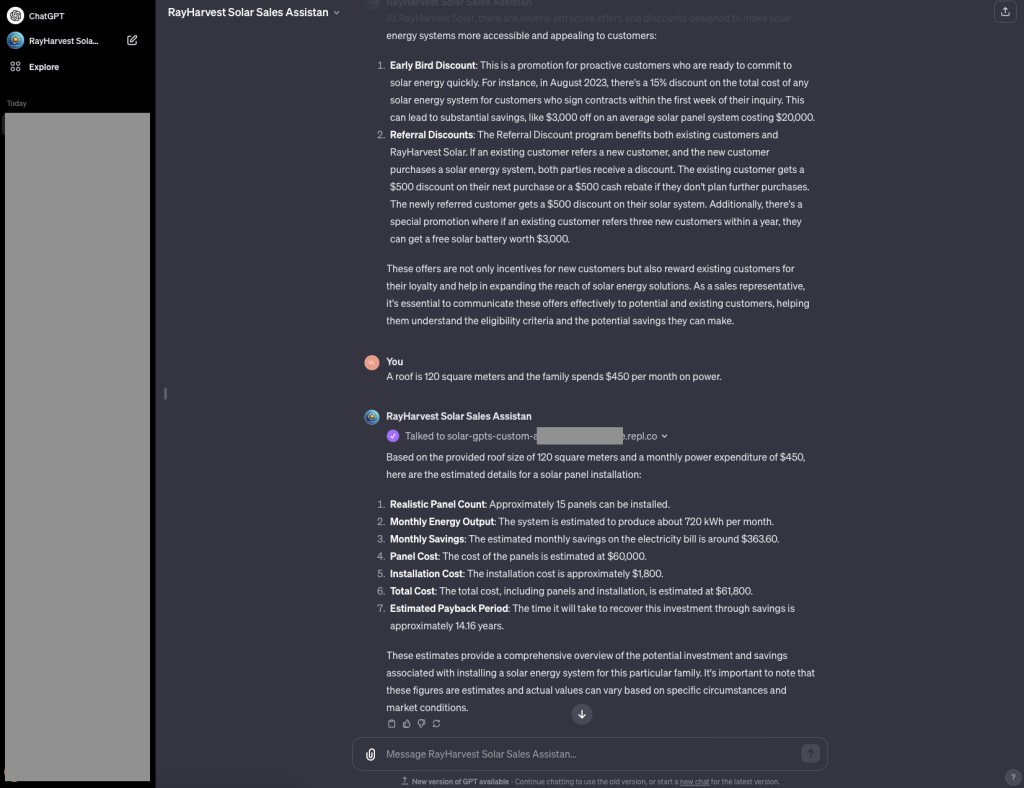
Testing the Assistant
The assistant seems to work great answering questions based on the provided knowledge base as well as doing calculations with a help of external service.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this tutorial has demonstrated the power and versatility of custom GPTs within OpenAI’s framework. By walking through the creation of ‘Solar Sales Assistant’, it was shown how integrating a knowledge base and custom actions can significantly enhance the functionality of GPTs. This tutorial not only provided a step-by-step guide but also offered valuable resources through a template, making it easier to replicate and adapt this functionality for own needs. Whether to streamline company processes, enhance customer interactions, or simply explore the capabilities of AI in business, the insights and tools provided here are a robust starting point.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.